Acidic Hydrolysis of an Amide Produces Which of the Following
In which of the following types of lipids are both ester and amide linkages present. The process can continue until thousands of units have joined resulting in large proteins.

18 6 Hydrolysis Of Amides In A Reverse Reaction Of Amidation Hydrolysis Occurs When Water And An Acid Or A Base Split An Amide Learning Goal Write Ppt Download
The main difference between phosphate and phosphonic acid arises from the higher stability resistance towards.

. The pH for reactions which form imine compounds must be carefully controlled. The nucleophilic conjugate base of this acidic nitrogen species is then prepared by treatment with sodium or potassium hydroxide and this undergoes an S N 2 reaction with a 1º or 2º-alkyl halide. C they are formed when an acid reacts with ammonia.
The reaction of aldehydes and ketones with ammonia or 1º-amines forms imine derivatives also known as Schiff bases compounds having a CN function. Since B has been formed upon heating compound A with aqueous ammonia the compound A is an aromatic acid. Consider the following acidbase reaction.
Acetic acid CH 3 COOH is an acid because it donates a proton to water H 2 O and becomes its conjugate base the acetate ion CH 3 COO H 2 O is a base because it accepts a proton from CH 3 COOH and becomes its conjugate acid the hydronium ion H 3 O. Different carboxylic acid derivatives have very different reactivities acyl chlorides and bromides being the most reactive and amides the least reactive as noted in the following qualitatively ordered list. Phosphonic acid mimics the phosphate group which is omnipresent in nature but also the tetrahedral transition-state intermediate encountered for instance during the hydratation of carbon dioxide by carbonic anhydrase or during the hydrolysis of amide.
Glutamine is the only one of the 20 amino acid residues that could serve this dual function since asparagine would not reach far enough into. The reactions involved are given as follows. A each reactant molecule contains an amide group.
An amide bond joining two amino acid units is called a peptide bond. Acid-base-catalyzed hydrolysis reactions and processes are very commonone example is the hydrolysis of ester derivatives or amide derivatives. D they are produced by basic hydrolysis of an amine.
Occupational exposure to asparagine may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where asparagine is produced or used. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group on the left and a reactive carboxyl group on the right. E they are formed when an acid functional group reacts with an amine functional group.
If Nuc-H is water the reaction is often called hydrolysis if NucH is an alcohol the reaction is called alcoholysis and for ammonia and amines it is called aminolysis. It is benzoic acid. More than one correct response.
The products of the hydrolysis of an oil are three fatty acids and a. Finally the activating group is removed by hydrolysis phthalimide or reductive cleavage sulfonamide to give the desired amine. Asparagine is widely distributed in nature in both plants and.
Complete the following reactions. Why cannot aromatic primary amines be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide. Expected to be an acid amide.
An amino alcohol c. The steroid nucleus common to. B they are produced by reaction between an amide and an ester.
The amide group of the Q61 side chain H-bonds to the carbonyl group of the GAP arginine finger helping to position it in the active site while its side chain carbonyl group accepts an H-bond from the nucleophilic water molecule. However the rate of this reaction under environmental conditions is not known. The hydrolysis reaction occurs when the nucleophilic reactant a nucleus-seeking agent eg water or hydroxyl ion attacks the carbon of the carbonyl group of the ester or the amide using an aqueous base medium since hydroxyl.
These can react with additional amino acids to lengthen the peptide. Asparagine contains an amide functional group which may be susceptible to hydrolysis. The reverse of an acidbase reaction is also an acidbase.
Water is eliminated in the reaction which is acid-catalyzed and reversible in the same sense as acetal formation. A long-chain alcohol b.
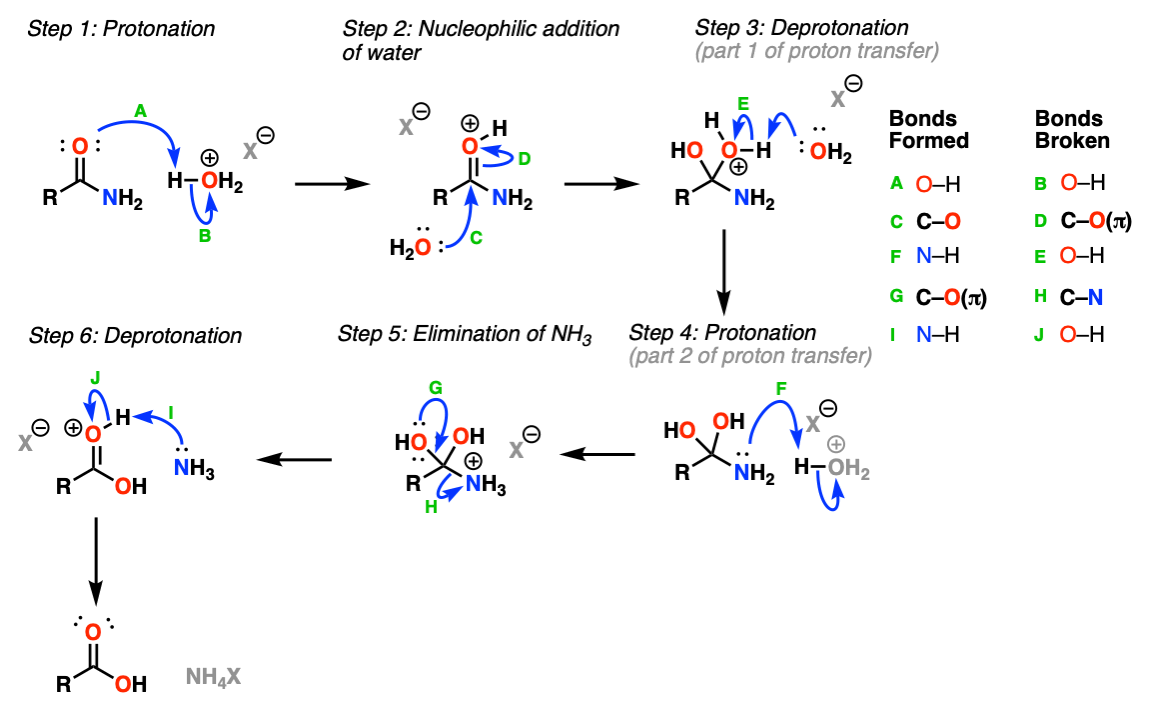
Acidic Hydrolysis Of Amides Master Organic Chemistry
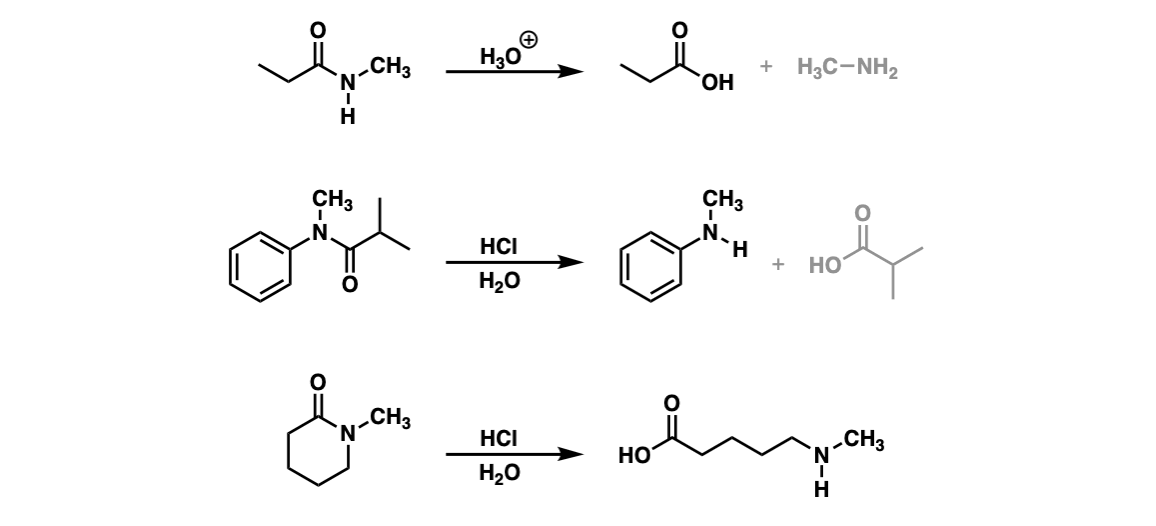
Acidic Hydrolysis Of Amides Master Organic Chemistry
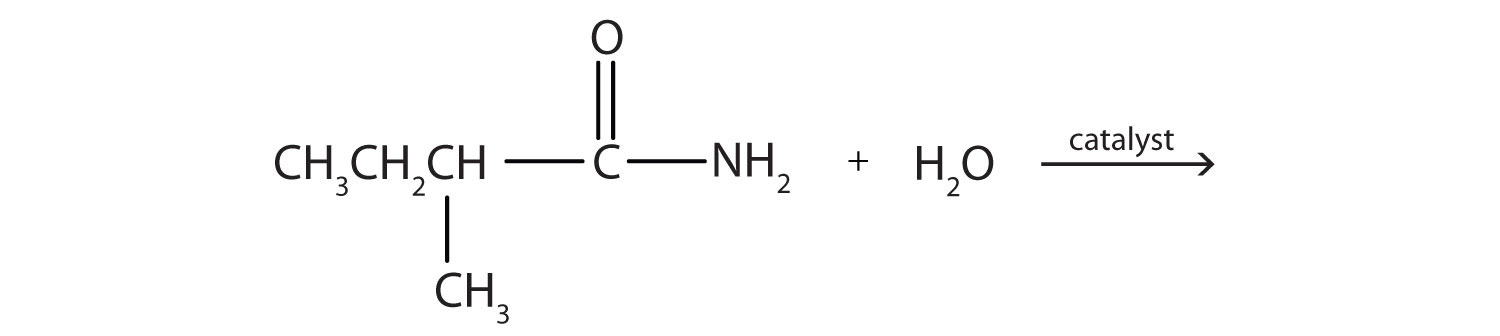
No comments for "Acidic Hydrolysis of an Amide Produces Which of the Following"
Post a Comment